Consultation
86-23-68614805 86-23-68614806

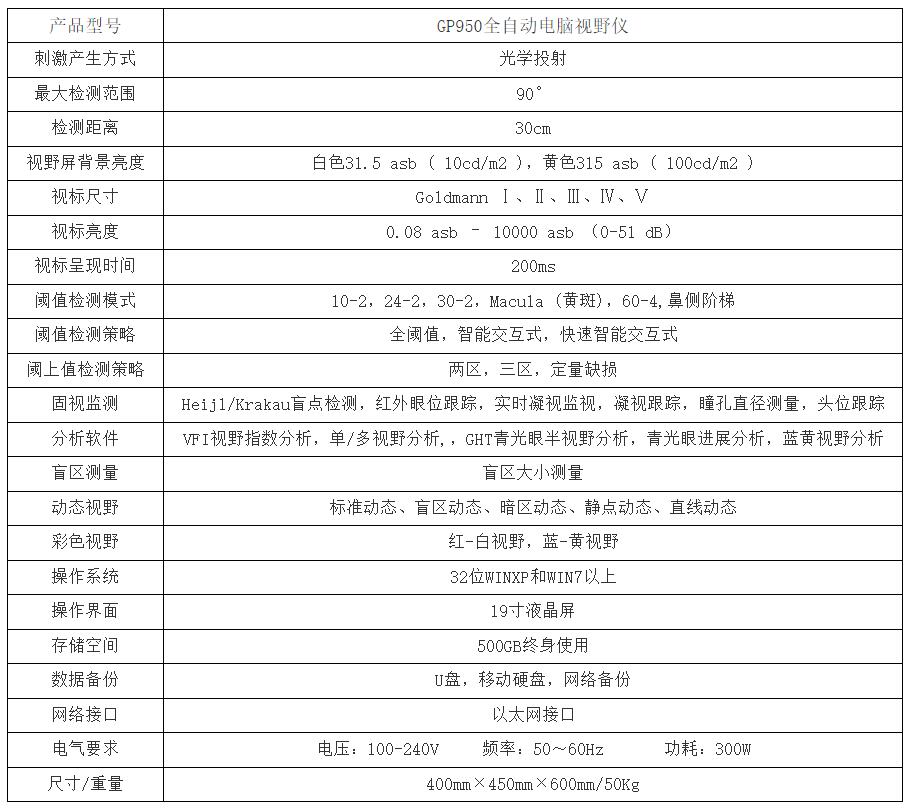
Fully implement Goldman standards
The brightness, size, and background brightness of the visual aids strictly follow the Goldman standard.
Comprehensive fixed vision monitoring
Heiji Krakau physiological blind spot monitoring
Real time video monitoring
Gaze tracking
Head position tracking
Automatic measurement of pupil diameter helps you effectively avoid the impact of pupil effect on visual field detection.
Efficient inspection strategy
The application of interactive operations combined with intelligent analysis strategies makes detection more efficient without reducing the accuracy of detection results. The threshold testing program within the 30 ° range can be completed in just over 3 minutes, and it brings you high-quality inspection reports.
Driver's monocular field of view inspection procedure
The design principle of this program is based on the American standard driver inspection program and adds a horizontal field of view inspection range (160 °)
Nasal visual field examination range: 72 °
Temporal visual field examination range: 90 °
Upper visual field examination range: 40 °
Scope of visual inspection below: 60 °
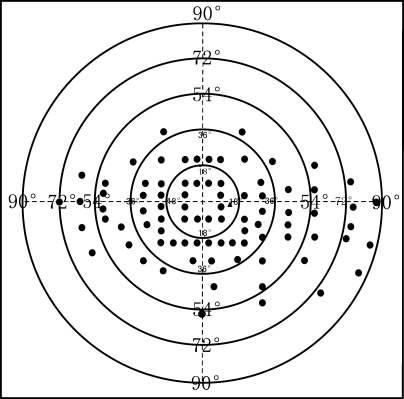
Regarding the correct scope of visual inspection in Order 139 of the Ministry of Public Security:
A monocular horizontal field of view reaching 150 degrees (checking only the horizontal line of view is not enough, the upper and lower fields of view should also meet the requirements):
Above view reaches 40 °
View below reaches 60 °
Application of visual field for glaucoma
SWAP short wavelength visual field examination:
Glaucoma causes damage to color vision earlier in the short wavelength range. Early glaucoma often selectively damages the blue cone cells. SWAP short wavelength visual field examination using a 440nm blue V visual standard combined with yellow background light can detect earlier visual field defects in glaucoma.
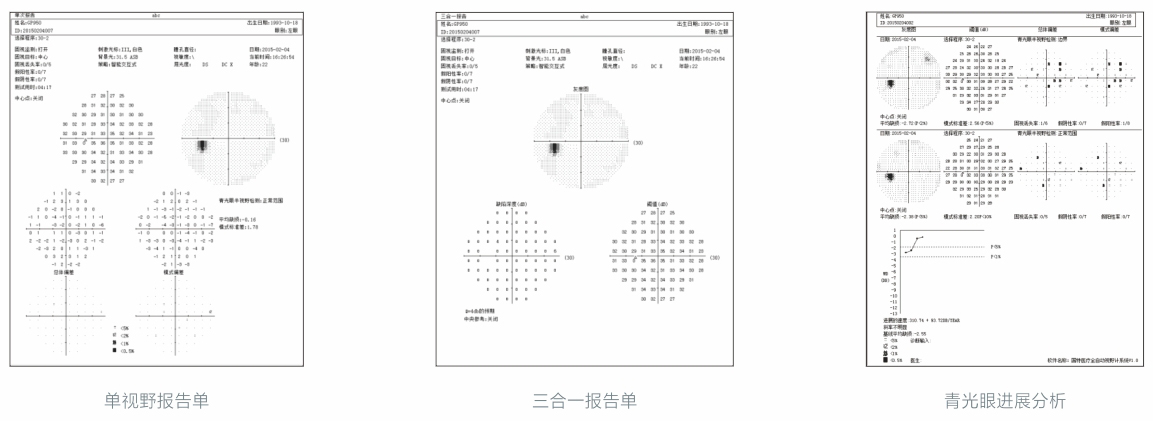
Glaucoma half field analysis:
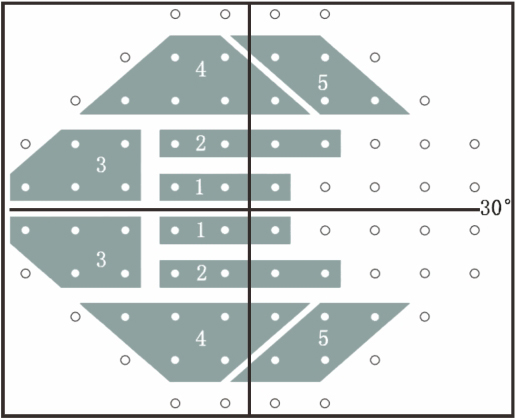
The field of view analysis method specifically designed for glaucoma divides the upper and lower half of the field of view into 5 corresponding areas in the central 30 ° area, with the horizontal meridian as the boundary. By comparing the corresponding areas and using different discrimination criteria, it indicates whether the field of view is within the normal range, boundary, general sensitivity decline, or beyond the boundary.
Analysis of glaucoma progression:
Compare the first two results of several visual field examinations performed by patients at different times with the baseline, and the subsequent results (up to 14 times) with the baseline, create a probability map of changes, and calculate the significance level of MD changes. Progress analysis provides point-to-point comparative analysis, allowing for the analysis of smaller visual field defects, thereby detecting changes in visual field earlier.